Mean vs Median
Mean and median are two different ways to find the middle or typical value in a group of numbers. 📊
Brief Introduction
When we have a list of numbers, we often want to find one number that best represents the whole group. The mean (average) and median (middle value) are two common ways to do this. It's like trying to find the typical score in a class or the usual amount of pocket money in a group of friends.
Main Explanation
Understanding Mean 📈
Mean is like sharing everything equally. If five friends have different amounts of candy (2, 3, 4, 4, 7), adding them all up (20) and dividing by how many friends there are (5) gives you 4 candies each. That's the mean!
Understanding Median 📊
Median is the middle number when values are arranged in order. It's like lining up students by height - the person in the middle is the median height. With numbers 2, 3, 4, 4, 7, the median is 4 (the middle number).
When to Use Each 🤔
Mean is great for balanced data, but can be thrown off by extreme values. If one friend has 100 candies, the mean would jump up dramatically. Median isn't affected by these extreme values, making it better for uneven data like house prices or salaries.
Examples
- 🏠 House Prices: In a neighborhood with houses worth $200k, $210k, $220k, $225k, and $1M, the median ($220k) better represents a typical house than the mean ($371k), which is pulled up by the expensive house.
- 📱 Screen Time: If your daily phone usage is 2, 3, 3, 4, and 12 hours, the median (3 hours) better shows your typical usage than the mean (4.8 hours), which is affected by that one long day.
- 💰 Allowance Example: Five kids get weekly allowances of $5, $5, $6, $6, and $20. The mean ($8.40) is misleading, while the median ($6) better shows what most kids receive.
How Feynman AI Guides Your Learning
- Choose Any Concept: Start from a topic you want to master — browse curated subjects or enter your own.
- Learn Essentials: Skim clear, structured explanations, key terms and common pitfalls to form a solid mental model.
- Explain & Get Feedback: Record your explanation (voice or text). Get instant analysis on depth, clarity, structure and example quality.
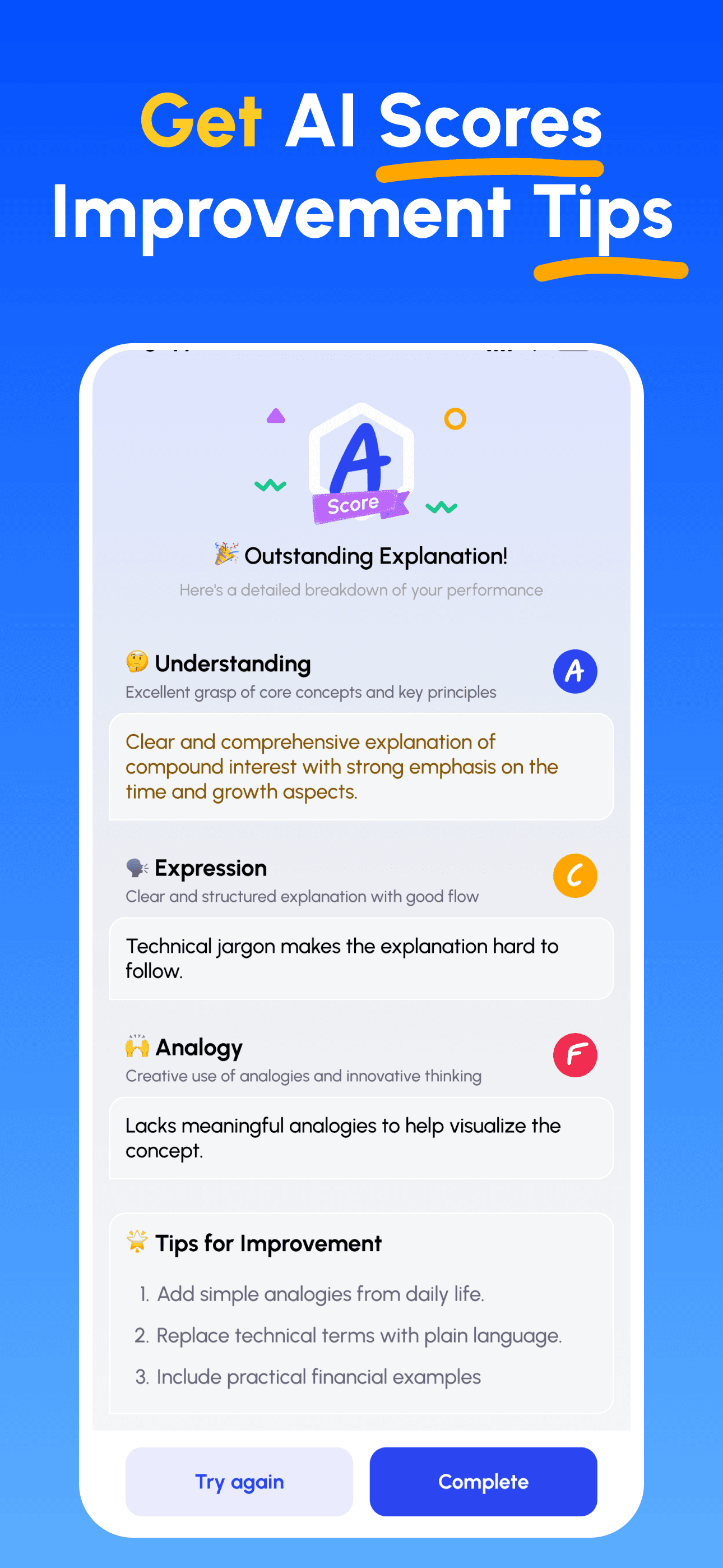
- Review Scores & Improve: Follow targeted tips, refine your explanation and iterate until you can teach it simply.
Download Feynman AI Now
Start your learning journey today!